Integrating QA-Board with your CI
CI tools run automated scripts and tests everytime someone pushes a new commit.
tip
If you don't have a CI, follow those instructions to use GitlabCI.
This said, you can still view your results in the web application by using qa --ci run/batch. Note: It will only work with commits that were pushed to gitlab!
Requirement
- Make sure your Gitlab project has an integration with QA-Board. If you're not sure if/how, review the setup guide. You should be able to see your project in the QA-Board web application.
Running QA-Board in your CI
- Have your CI launch QA-Board: With GitlabCI, you would do something like:
qa-tests:
stage: test
script:
# assuming you defined a batch named ci
- qa batch ci
note
You CI is responsible for setting up an environment ($PATH...) in which qaboard is installed! Consider using docker, or sourcing a configuration file...
- Push a commit to Gitlab. If your CI is successful, the commit will appear in your project's page:
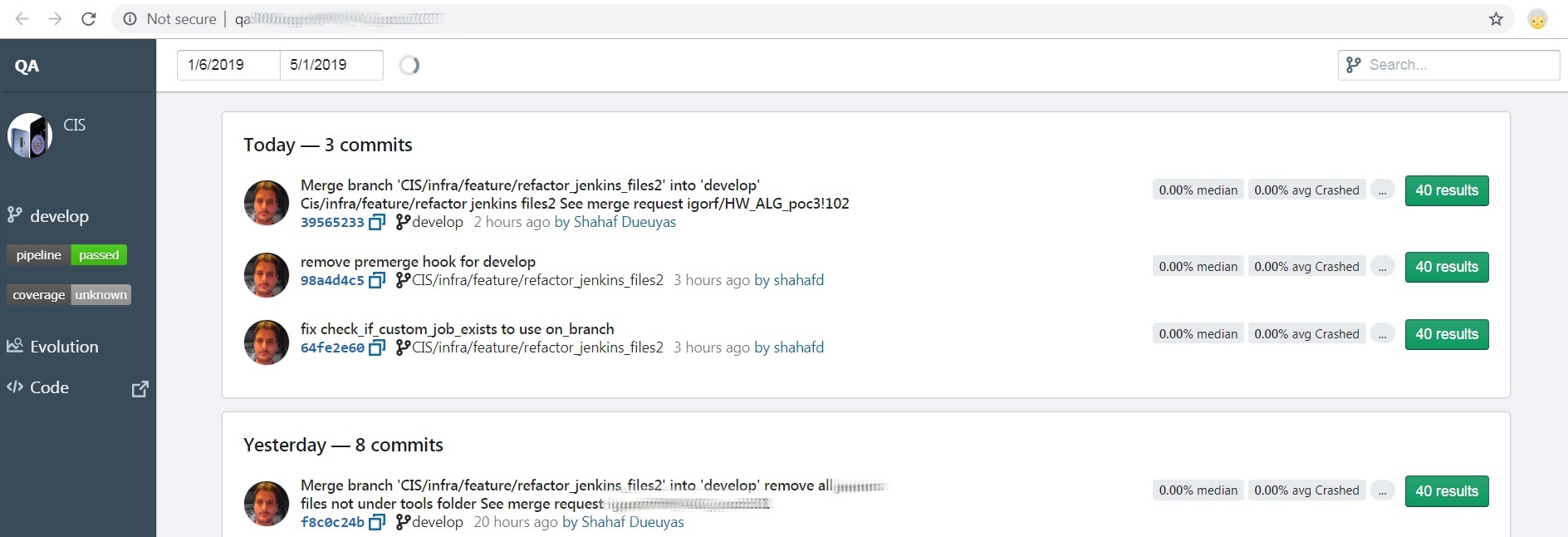
Example with GitlabCI
QA-Board knows how to work with the most common CI tools: GitlabCI, Jenkins...
stages:
- build
- qa
build-linux:
stage: build
script:
- make
- qa save-artifacts
qa-tests
stage: qa
script:
- qa batch ci
Optionnal CI helpers
QA-Board is not a CI tool, but it provide some utilities to run code only in some branches:
caution
This logic is usually better expressed in your CI tool itself. But if you're stuck with stone-edge tooling sometimes you roll your own.
# ci.py
from qaboard.ci_helpers import on_branch, run_tests
@on_branch('develop')
def my_tests():
pass
# Also supported:
# @on_branch(["develop", "master"])
# @on_branch("feature/*")
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_tests()
python ci.py